Open Channel Flow Meter is a channel used to drain water on open ssitem where it is widely used to drain water into rivers or sewage treatment reservoirs. For this we can use flow meters with this type of
- Level Sensor ultrasonic
- Velocity Sensor ultrasonic
- In Line Electromagnetic flow meter
- Clamp on Ultrasonic flow meter
- Open Channel Flow Meter With Sensor Level
- Open Channel Flow Meter using sensors Ultrasonic
- Open channel flow meter using electromagnetic flow meter
- Open channel using Clamp on ultrasonic flow meter
- Installation of Open Channel Flow Meter wastewater.
- How the Open Channel Flow Meter works
- Ultrasonic Counter
- Electromagnetic principles
- Lever-pendulum flow meter
- Open Channel Flow Meter waste measurement unit
- Sewerage meters US800 are used to calculate domestic and industrial wastewater, household waste.
- External device connectivity options for US-800 wastewater meters
- Advantages and Benefits of the US-800
- Scope of US-800 delivery as standard:
- Description of accessory: ELECTRONIC UNIT US-800
- US-800 digital interface
- Description of components:
- Wastewater meter: suitability for installation
- Problems that may arise when taking measurements of open channel flow meters
- Methods for wastewater accounting (Open Channel Flow Meter)
- Types of wastewater flow meters: level gauge, radar flow meter, Doppler, cross correlation, electromagnetic, pulsed time, lever and other flow meters.
- Selection of flowmeter type for wastewater measurement unit (Open Channel Flow Meter)
- Installation of submersible sensors for wastewater meters (Open Channel Flow Meter)
- Possible problems when using a waste measuring device with a soak sensor
- Open Channel Flow Meter Review of the most popular models and manufacturers.
- Open Channel Flow Meter Price for wastewater flow meter.
- Method for drain head pressure accounting Open Channel Flow Meter
- Accounting for channels without pressure
Open Channel Flow Meter With Sensor Level
In this type of level sensor serves to capture the water level continuously and real combined with vitot calculations or other can also be rectangular shape. Level sensors can use ultrasonic or radar level types and others.
The principle of this Open Channel flow meter system is the cross-sectional area of the channel multiplied by the flow speed that refers to velocity due to the difference in height.
Catalog HD1200 open channel
Open Channel Flow Meter using sensors Ultrasonic
In this type uses 2 sensors, namely ultrasonic sensors to detect flow velocity and ultrasonic level sensors to detect water levels continuously. With the know of flow velocity and water level then through the flow transmitter is known flow rate / deit water.

Open channel flow meter using electromagnetic flow meter
This type can actually be used by modifying the trench, namely by closing the aparit at the end and in the hole with a pair of water pipes. Electromagnetic flow meter is installed in the output pipe with a modified pipe installation note by maintaining the pipe on the water system in full so that the electromagnetic flow meter can function optimally.
Open channel using Clamp on ultrasonic flow meter
For this type, the principle is the same as using electromagnetic flow meters but the advantages of ultrasonic clamp on flow meter sensor is enough to be attached to the surface outside the pipe and in the clamp. Thus the discharge of water in ipa can be detected by ultrasonic transducer and known flow rate.
Installation of Open Channel Flow Meter wastewater.
Providing residential development with utilities is an important aspect to improve the comfort of life. Living in each house is characterized by a large consumption of water for household needs without further disposal: watering the garden, garden, water consumption by humans and animals, etc. In order not to pay for wastewater services for the water consumed, the installation of a wastewater meter is required. Counters will show that in reality less water goes into the sewer than it does entering the house.
A wastewater flow meter is a high-tech device that has electronic components in its design and ensures measurement accuracy and reliability. Workmanship of the instrument base and device components allows you to work in a chemically aggressive environment, without losing the reliability and accuracy of measurements.
How the Open Channel Flow Meter works
Counter sewerage is divided into the following types, depending on what operating principles underlie their work:
- uSG
- electromagnetics;
- tuas-pendulum.
According to the measurement method, waste measurement devices are divided into two types:
- Accounting for the rate of effluent flow in the pipeline. The number of channels is determined depending on the size of the channel.
- Calculates the flow rate along with the rate of effluent flow in the pipe. The amount of wastewater is determined based on the “area-speed” principle.

Ultrasonic Counter
High precision instruments to measure the amount of liquid waste. Measurements are made using sensors according to the “area-speed” method, which is easy to install in collectors. They are used in open channels, gravity systems, un pressured pipelines, in the industrial sector for commercial measurement. When the instrument is equipped with a hydrostatic sensor, in addition to monitoring the discharge volume, monitoring is carried out to fill the sewer network.
Installation is carried out inside a pipe or duct without additional construction work.
The operation of ultrasonic sensors is based on measuring the difference in travel time of ultrasonic vibration pulses in the direction of fluid flow movement and against them. The sensor (piezoelectric transducer) is installed on the measurement section, which initiates the excitation of this pulse.
Ultrasonic sensors are installed at an angle relative to the flow cross-section. Speed can be measured by one or two rays of ultrasonic vibration. Sensors operate alternately, first as an emitter, then as a receiver. The movement of the liquid causes a complete propagation time change of the signal along the flow and against it. Based on the signal received, the speed and volume of effluent in the pipe are determined.
The advantage of this type of device is its versatility, the possibility of installation in any geometric pipe network with a diameter of up to 9 m. Measurements are made in all directions of flow. Construction of additional wells or measurement rooms for the installation of the device is not required.
Disadvantages of the device include the need for continuous cleaning of sensors. Channel inhomogenity, the presence of bubbles, suspension reduce the reliability of indicators. The measurement error reached 5%.
Electromagnetic principles
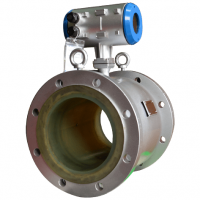
It is a simple yet reliable instrument for measuring the volume of wastewater, including untreated ones. It is used on the sewer system of gravity and pressure, provided the pressure in pressurized wastewater does not exceed 40 bar.
The principle of operation of wastewater volume meters is based on the measurement of electric force of motion (EMF), which occurs in wastewater when it passes through an artificial magnetic field. The flow rate of the fluid is directly proportional to the EMF that appears, which is converted into a signal received on the display of the controller. Measuring the volume of effluents is only possible if they conduct an electric current, since the action of the device is based on Faraday’s law (magnetic induction). The liquid that passes through the magnetic field acts as a movable nucleus. It initiates an electric current, depending on the speed of the effluent.
The advantage of electromagnetic devices is their versatility, allowing you to measure any type of liquid waste that drains electric current, including untreated wastewater. The instruments stablely show high-precision data, provided there is its own cleaning electrode system.
Note! Disadvantages include unstable operations in the presence of strong electromagnetic interference. The cost of the flow meter depends on the diameter of the pipe or duct, as the design of the main converter should always be full.
Lever-pendulum flow meter
The scope of the device is a pressure-free open and closed sewer. The principle of operation is to measure the average rate and rate of flow. Measurements are made continuously. Channel dimensions, information about the current value of the flow level makes it possible to calculate the current value of the cross-sectional area of the effluent. Wastewater volume is defined as the product of the rate of discharge flow passing through per unit of measurement time. Device productivity is defined as a cross-sectional product of flow at its speed.
This device is a device with a lever mounted on the axis, where a round-shaped buoy is rigidly attached. At the end of the lever is mounted the angle of the lever deviation sensor relative to the vertical to horizontal line. In the absence of aqueducts, the lever is in an upright position. In the presence of the channel, the float goes up or down, changing the angle of tilt depending on the level of the line in the pipe. Through the reading of the angle of tilt, the level of disposal is determined.
To measure speed, another unit is used, namely a rotary knife made of stainless steel. The knife is fixed on the axis. One end of the free blade is lowered into liquid waste. A sensor is mounted on the axis, which indicates the speed of flow with the angle of deflection of the blade, depending on the strength of the current.
The device provides high accuracy of wastewater accounting measurement parameters, regardless of contamination in pipes and other factors.
Before choosing a flowmeter model, you need to know what requirements are presented for the sewage system and what type of water pipe is used.
Sewerage networks can be divided into open and closed. Closed networks are divided into pressure and non-pressure. Open channels are also not pressurized. Through the pressure channel, the effluent moves under the influence of the pump, in the pipe without pressure and open, by gravity due to the tendency of the pipe.
For measurements in pressure pipes, instruments with sensors are used. Electromagnetic or ultrasonic flow meters are selected based on the calculation of the estimated cost of effluent.
Establishing the calculation of wastewater in gravity pipelines is a more difficult task. Open or closed channels are characterized by the movement of waste by gravity under the influence of gravity at low speeds.
Instruments that measure only liquid levels provide evidence for further calculation of effluent volume taking into account channel cross-sectional data. For open channels, use a lever-pendulum flow gauge.
More accurate results are obtained by second type instruments, measured according to the “area-speed” principle. The level of fluid in the channel without pressure is not constant. In private homes, sewerage can occur periodically, there the sewer will be dismantled most of the time, therefore, data is used on the flow area, its speed over a period of time.
To measure speed in a closed channel without pressure, ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters are used. The specific model is selected depending on the diameter of the pipe.
Open Channel Flow Meter waste measurement unit
A wastewater measurement unit is a combination of ways to measure the cost of wastewater, a well, to place its measurement and maintenance device, and the part of the pipe where the measurement is taken. The measuring instrument consists of a primary transducer (sensor) and a secondary transducer where the processing, storage, and display of the measured information takes place. Wells are specially constructed in this section of the pipe. The pipe should be directly in the runoff measurement section.
Before choosing the type of flowmeter, an assessment is required about the feasibility and feasibility of installing the measurement device and the choice of device installation location.
When meter units are installed in individual buildings, places should be selected to a point of connection with a common sewer.
When selecting a gauge, the tool must record the value of the flow rate of waste across the flow range for the diameter of the existing pipe. Measurement accuracy should be high, errors of no more than 5% are allowed. The accounting system must accumulate all information, providing information about the total cumulative volume, measurement period, and downtime. The power supply to the flowmeter should be uninterrupted with backup resources.
The part of the pipe where the meter is installed must be direct. The flow meter should be placed at the lowest part of the individual sewer network, where the maximum charging of the pipe is located.
For each node, a project is required, coordinated with the departments and organizations serving the sewer network. After receiving all permissions and completing the project, the subscription service agreement is concluded.
The US-800 ultrasonic flow meter of wastewater and wastewater (household, wastewater, and industrial wastewater) is designed taking into account the specifications of operating measuring devices in the Russian Federation, has built-in protection against excess voltage and interference in the network, and the main converter is made of stainless steel! Available with ready-made ultrasonic transducers for diameter: 15, 25, 32, 50, 65, 80, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 800, 800, 900, 1000, 1200, 1400 mm!
It is custom made and ideal for use by water utilities, in pumping stations, utilities, energy, industry!
Sewerage meters US800 are used to calculate domestic and industrial wastewater, household waste.
The exact same set of flow meters is used to measure the volume and consumption of domestic pressurized water and wastewater, chemical waste, fecal wastewater, etc., for water measurement.
Flow meters for wastewater must be installed in accordance with the following rules:
ATTENTION! The main condition for the correct operation of the US-800 water flow meter is the complete filling of the UPR section with liquid.
To avoid possible measurement errors and failures due to gas or air inclusions, the following recommendations should be followed:
- On very long horizontal pipes, it is advisable to install a UPR in the section that has a climbing angle (see Figure. A)
- When supplying or flowing liquids with gravity, UPR installation is carried out in underrated parts of the pipe (see Figure. B)
- Avoid installing control units at the highest point of the pipe (see gbr. C)
- Do not attach perpendicular to the downhill part of the pipe, which has a liquid free to flow into the atmosphere (see Figure. D)
- Avoid installing inqueducts on pump inqueducts
- When installing a UPR, the probe field should be horizontally oriented with a deviation of no more than 25 degrees. (See figure d)

External device connectivity options for US-800 wastewater meters

Advantages and Benefits of the US-800
Galvanic insulation of primary converters (pipes) of electronic units. METERS ARE JUST CURRENTS IN RUSSIA!!
- Immunity and noise safety are high in any operating conditions, even the most difficult.
- Flow measurement channels on two-channel devices are also galvanizedly isolated– this does not include their reciprocal influence (a phenomenon observed in two-channel devices with multiplexing). Rs485 digital output, current output of 4-20 mA is galvanizedly isolated.
- More than 10 years of successful operating experience has demonstrated the stability of the device even with lightning strikes inside pipes, not to mention welding.
- Intelligent self-diagnosis system:
- Continuous monitoring of device performance and reliability of results obtained, filtering, and neutralizing interference. Network filter:
- Protection against interference and pulses at supply voltage, automatic protection against more voltage, excess heat. Ultrasonic function self-cleaning piezoelectric transducers. - Flow measurement mode options: modulo, with reversals, with options only one way forward.
- The base of specially selected elements is the production of leading foreign companies – PHILIPS, TOSHIBA, INTEL, etc.
- It doesn’t make you lose pressure! Full bore, free of mechanical/moving parts.
- Measure the section for any diameter!
- High-level protectionfrom external influences (IP65/IP68): – The ability to install measurement sections in unregulated climatic conditions, as well as in fully flooded wells and in depths.
- It can be programmed flexiblybased on the requirements of the production facility.
- Attractive appearance:
- Modern case with protection against external influences of IP 65.
- Reliable connectors.
- The programming keyboard is closed by a tightly closed transparent cover. - Lack of galvanic electricity supply in non-volatile memory.
- No special treatment is required for the entire operating period (more than 25 years).
- Free warranty service for 2 years!
- Uninterrupted verification procedure (without dismantling the main converter, approved by the Standards of the State of the Russian Federation)!
- Testing interval -4 years.
- Guarantee -2 years.
ALL PRODUCTS ARE CERTIFIED!
| USER FLOW METER US-800 | EB serves 1 single beam control, one measurement channel, 2 sensors (1 beam) embedded in the control | EB serves 2 single beam control units, two independent measurement channels in one electronic unit, 2 sensors (1 beam) embedded in each control unit, convenient in multi-channel systems, in composite heat meters | EB serves 1 double beam control, one measurement channel, 4 sensors (2 beams) embedded in the control, it has an accuracy improvement of 0.5-1%, requiring a minimum of straight parts during installation. | ||
 |
 |
 |
|||
| DN 15 to 1400 mm | DN 15 to 1400 mm | DN from 50 to 1400 mm | |||
Scope of US-800 delivery as standard:

Description of accessory: ELECTRONIC UNIT US-800
 Electronic units have large LED indicators (segments), which display flow rate (m3/h), volume (m3), time (hour) of device uptime.
Electronic units have large LED indicators (segments), which display flow rate (m3/h), volume (m3), time (hour) of device uptime.
The electronic unit is the home of plastic instruments for installation on the walls. Supply voltage 220V. Maximum power consumption up to 7 watts. The ambient temperature at the installation site is from +5 ° С.
In addition and on orders:

US-800 digital interface
| Possible digital output of US-800 electronic units versions 11, 13, 21, 23, 31, 33 |
|
| RS485 digital interface Support for RS485 data transfer protocol: DCON, Modbus (optional) | |
| The load capacity of electronic units allows you to combine up to 32 flow meters in a single network segment. Using an RS485/RS485 repeater, the network can be expanded to 256 pcs flow meters. | |
Description of components:
 The UPR ultrasonic flow converter (with the probe already installed) is a segment of pipe, at the end of which two flanges are welded, and the probe is located in the middle. The ambient temperature at the installation site is -40 to +60°С.
The UPR ultrasonic flow converter (with the probe already installed) is a segment of pipe, at the end of which two flanges are welded, and the probe is located in the middle. The ambient temperature at the installation site is -40 to +60°С.
Pipes with a diameter of 250-2000 mm are also offered a control valveless kit – with KMCH – a set of sensors and mounting components to be inserted into the pipe (or control valve manufacture) at the operating site. Kits with KMCH require a capable installation! A UPR or KMCh is required in the kit!
A UPR consists of two types, depending on the number of measurement beams: a single beam and a double beam. Also differing in connection methods (mottled or welded)and manufacturing materials 12X18H10T (stainless steel) and st20 (black steel):see table below.
| ULTRASONIC CONVERTER IMPLEMENTATION OF CONTROL EXPENDITURE | |||
| ONE SINARinset a pair of sensors with diameter. STANDARD EXECUTION.  |
DOUBLE beamS Include two pairs of sensors along the chords. + IMPROVED ACCURACY, + RELIABILITY, + MINIMUM LIVE INSTALLATION SITE  |
note: Maximum pressure, max temperature, Dust protection level and humidity. | |
| UPR 15, 25 stainless steel 12X18H10T, koneksi berulir  |
1,6 MPa +120 ° C, IP65 |
||
| UPR 15, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65 | UPR 50, 65, 80, 100 stainless steel 12X18H10T, koneksi flensa  |
1,6 MPa +120 ° C, IP65 |
|
UPR 80, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300 |
UPR 150, 200, 250, 300 stainless steel 12X18H10T, koneksi flensa  |
1,6 MPa +150 ° C IP65 |
|
 |
UPR 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1200, 1400 steel20, connection leads  |
1,6 MPa +150 ° C IP65 |
|
UPR 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1200, 1400 |
UPR 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1200, 1400 steel20, wafer-less for welding  |
1,6 MPa +150 ° C IP65 |
|
KMCh one beam. 200-2000 |
KMCH double beam. 200-2000tubeless version, UPR not included.
Steel20, set of mounting components (boss, nut, gauge) for pipe installation at the site of operation
|
2,5 MPa +150 ° C IP65 |
|
| Note: 1) All flange connections can be equipped with mating and fasteners (at an additional cost). The material of all flanges is steel20, flanges according to GOST 12820-80. The traditional method of calculating wastewater is to determine the volume of one meter on a water pipe. The logic of this approach is simple – it is believed that most of the water that has arrived at the point of withdrawal falls into the sewer. However, this is not always the case. 
Some water can be used for irrigation or other needs without subsequent diversion into the sewer system. Devices such as wastewater meters are particularly useful in companies where the amount of wastewater that goes into the sewer is much less than the volume of water coming in. Modern measurement devices are high-tech products with electronic components. The device provides accurate and reliable measurements.
According to the principle of operation, wastewater meters are divided into two types:
In addition to stationary gauges, portable devices are used that are used to temporarily replace removable flowmeters. Portable meters are equipped with ultrasonic sensors. The device can work all day on battery power, and at night recharge the battery. With the help of adapters, their uninterrupted power can be set up. Wastewater meter: suitability for installationBefore choosing the required type of flowmeter, it is necessary to evaluate the feasibility of such measurements and choose a place for the installation of the device. In cases where facilities that are wastewater producers are in dense development areas, accounting organizations for waste are often impossible. A special report was issued to confirm the technical impossibility of installing a flowmeter. If the decision to install a flowmeter is made, then the type of device should be determined depending on the characteristics of the object. Usually, the flowmeter is installed on the existing network in a special well.
|
|||
This is against the rule that the measuring instrument must be installed in a straight line.

Problems that may arise when taking measurements of open channel flow meters
When setting up accounting, you can find two problems that affect measurement accuracy, namely underdevechment and siltation.
Reasons for the remote occurrence:
- accumulation of solid waste in the pipes, forming blockages;
- destruction of individual parts of the pipe;
- the presence of a bias in the opposite direction to the flow of water;
- if the inset is made at a lower level than the exhaust surface in the city collector, water will appear from the collector’s side.
Blockages can be eliminated by cleaning the sewage system, and other problems are solved by making repairs.
Causes of siltation:
- sand enters the pipe;
- inadequate slope of the pipe;
- destruction of part of the pipe, as a result of which the soil enters the sewer.
To avoid measurement inaccuracies, before calculating the volume of wastewater, it should be considered to bring the system in full order.
To get the correct stock accounting results, it is necessary:
- install the device in a straight section;
- when the aqueduct moves due to gravity, the flow meter must be installed at the bottom;
- wastewater measurement units cannot be installed at the top of the network, as accurate measurement is only possible with maximum filling of pipes;
- if the sewer is freely discharged into the environment, then the meter cannot be installed at the bottom of the sewer system;
- the sensor field can deviate from the horizontal line by no more than 25 0.
Methods for wastewater accounting (Open Channel Flow Meter)
The wastewater in the sewer system can move along the pressurized and uncernished network.
In pressurized tissue, the fluid moves under the influence of the pump, and in the network without pressure by gravity, due to the slope of the pipe.

Measuring the amount of wastewater passing through pressurized tissue is not difficult. In this case, you can use a device that works based on the principle of water meter.
The difference in operating conditions is the presence of large amounts of pollution in wastewater and lower water flow rates. The selection of flow meters is carried out, taking into account the estimated rate of wastewater flow.
It is much more difficult to account for wastewater moving due to gravity. This movement is carried out at an insignificant speed under the influence of the force of gravity.
- instruments that measure exclusively the water level,
- a device that takes into account its effluent rate and speed.
The first type of flow meter is used for U-shaped lines and pipes. In channels of different shapes, standard bends are used.
For them, a formula developed empirically to convert waste levels into their consumption.
To measure the actual fluid level in the sewer pipe, you can use an external sonar transducer or an immersion device that takes into account the decrease in air pressure. By comparing the results of these two measurements, you can obtain accurate information about the volume of wastewater.
The use of devices that simultaneously take into account fluid levels and flow rates allows you to get the most reliable data about the amount of waste that goes into the sewer system.
Measurement of fluid flow (Q) in a pipe or duct cannot be done directly. For its calculations, the formula Q\u003d Ṽ * A is used, where A is the cross-sectional area of the flow, and Ṽ is the average speed.
In this case, the main and difficult task is to correctly determine the average speed of Ṽ, since the cross-sectional area of A is determined based on the shape of the channel (which can be taken from the construction documentation, or measured when making the unit of measurement) and the level of flow, measurements that can be done in various ways and, as a rule, are not a problem.
Types of wastewater flow meters: level gauge, radar flow meter, Doppler, cross correlation, electromagnetic, pulsed time, lever and other flow meters.
Currently, there are several methods for measuring the flow of wastewater in the pipeline without pressure and a large amount of equipment to address this problem. These methods include:
- Use it as a level meter flow meter mounted on a Parshal or Venturi tray, or directly above the channel or inside the pipeline. In addition, the average speed is not measured at all, but it is assumed that this value is constant and the flow rate depends only on the level.
- Radar non-contact flow gauge that measures the level and speed of surface runoff. The average flow rate is determined by multiplying the surface runoff speed by the constant coefficient.
- Ultrasonic flow measurements are based on the Doppler method, which measures the speed at various points of flow and calculates the average speed based on additional data entered on the roughness of the pipe wall, etc.
- A system that provides the transfer of the mode of operation of non-pressure pipes to the pressure. At the same time, the bent up part is mounted on the gravity pipe, ensuring 100% charging of the pipe, after which the flow measurement in this pipe is provided by an ultrasonic electromagnetic metering device or a full drill designed for pressure pipes.
- The dips ultrasonic cross-correlation flow meter measures the flow speed by layer and calculates the average value based on data on the speed distribution across cross-flow sections.
- A time-pulse flow meter (this method is also called transit time or transfer time) are two sensors located on opposite walls of a pipe or channel, which are each a receiver and a radiator. Sensors are directed at each other and send ultrasonic signals with a narrow focus towards the other. The axis that passes through the sensor is located at an angle of 45 to 70 degrees to the pipe axis. Moving with flow with flow, ultrasonic light travels the distance from one sensor to another faster than against current. Based on this, the speed of flow is determined.
There are several other types of wastewater meters, but they are not common due to their obvious weaknesses when working in wastewater.
These are, for example, electromagnetic point flow meters, sensors that measure in local flow areas. The disadvantage is that electromagnetic point sensors are able to operate continuously only in relatively clean water.
There are also devices that determine the current velocity based on the measurement of the angle of the pin deviation (lever) immersed in the flow. This method is quite simple, but any impurities on the surface of the river, especially in household waste (hair, cloth, etc.), immediately violate the testimony.
Selection of flowmeter type for wastewater measurement unit (Open Channel Flow Meter)
To determine the application of the above system under certain conditions, we consider its main advantages and disadvantages.
(1) Contactless Flow Meter Radar

Main advantages: simplicity and ease of installation and maintenance, which is determined by the fact that the distance sensor is located above the surface of the water and does not come into contact with the sewer. The device measures the level of surface runoff, which is a significant advantage over just the level gauge.
However, the small distribution of these systems is currently both in Europe and in Russia, as well as quite a lot of negative reviews, suggesting that they also have drawbacks. The main disadvantage is a very high error in measuring flow rate, reaching up to 30% and even up to 50%. Major errors are determined by the strong dependence of this measurement method on the surface state of the flow (of waves and ripples), as well as the absence of a clear relationship between the measured surface speed and the average velocity, which determines the volumetric flow rate of the liquid.
The use of radar flow meters is only recommended in cases where there is absolutely no possibility to install a more accurate device (submersible) – Doppler or cross-correlation. In addition, radar flow meters are quite expensive nowadays, and their use on commercial water meter nodes with low flow rates is impractical.
(2) Flowing meter for gravity channels based on level gauge
In addition to the above-described disadvantages inherent in non-contact radar systems, when using level meters to determine flow rates, the problem of lack of information about flow rates is added.
Such devices can operate relatively adequately in the absence of remote areas. But to ensure the absence of remote areas is very problematic. If they are not even present at the time of installation of equipment, then they can appear unexpectedly from time to time. Any clogging object or foreign body in the channel that produces a blockage. If the pipes from the company eject wastes to the city collectors, and the collectors operate in a large charging mode, there are also underdeveloped ones. If there is water, the error of this measurement method can reach hundreds of percent. If the water in the reservoir is stationary and levels remain high due to underdevelopment, the faults tend to be infinite.
In addition, the use of ultrasonic level gauges is not possible in the presence of foam, steam, fog, intense rainfall, large waves, etc.
The undoubted advantages of a flow meter system based on a level meter are its low cost, as well as ease of installation and maintenance. It is recommended to use this method either for technological (non-commercial) needs, or for commercial measurements on pipes and lines at low flow rates, when even large faults of the device do not cause substantial financial losses.
(3) Doppler wastewater flow gauge
Submersible Doppler flow meters measure the speed of particles in a stream based on the Doppler effect (measuring the frequency difference between the ultrasonic signal emitted and the reflected signal of the moving particle).

The problem is that in different layers the flow particles move at different speeds. Closer to the bottom or wall, the particles move slower, closer to the surface – faster, slower still on the surface. The distribution of velocity depends on many factors, including the size and nature of the base sediment, the roughness of the walls, the properties, speed and flow rate, etc.
Doppler sensors cannot determine at what level the particles are measuring their speed. Average speed in this case is defined as the product of the measured speed and calibration coefficient “K”.
In this case, calibration factors are usually selected according to the table depending on the material of the pipe wall or duct, the time from which the channel starts operating, etc. Significant assumptions have been used. Or the coefficient is determined during calibration during installation. But, in this case, it should be remembered that the actual dependence of the average speed on the measured is a nonlinear function of speed and level, e.g. Calibration done with some hydraulic characteristics will not be correct with other characteristics. In addition, the level of runoff contamination (the number of suspended particles per unit volume) greatly affects Doppler flow meter readings.
The Doppler measurement method provides much more accurate results than the use of a level gauge or non-contact radar flow meter, but at the same time the error can be 20-25%, with proper adherence to all operating manual requirements (confirmed by a number of comparative tests). However, in some cases, depending on certain hydraulic conditions, Doppler flow meters can provide good accuracy (2-5%).
Changing the non-pressure mode of operation from pipe to pressure is a fairly simple and beautiful solution for small diameter pipes.
 |
 |
 |
After installing the bent part of the pipe upwards in a non-pressure pipe well, the pipe is fully filled and goes into pressure mode. Measuring flow in a pressure pipe is a simpler and more fulfilled task. This can be done both by ultrasonic sensors and electromagnetic flowmeters, errors that can be 0.5-1.0%. However, in some cases, with a dirty drain, a blockage can form at the bend of the pipe upwards – as a result, the error due to the deposit increases (comparable to the growth of the deposit) and after a while the unit becomes out of service. Daily plumbing cleaning at the location of the meter unit seems unacceptable to the user. In addition, this method is difficult to apply and quite expensive on large diameter pipes. It is usually used on pipes with a diameter of less than 300 mm.
(5) cross correlation stock meters
The cross-correlation method was developed and patented by Nivus GmbH in 2000. This method is sometimes confused with the Doppler method, although it is not directly related to it. The cross-correlation method does not analyze changes in signal frequency when reflected from moving particles, but compares ultrasound photos taken at frequencies of 500 to 2000 units per second.

Based on this comparison of ultrasound photos, the movement of particles in each flow layer per unit of time is determined, i.e. the speed of all flow layers is determined. Thus, the average speed is calculated accurately based on direct speed measurements obtained above the flow layer. In this case, no initial calibration is required or takes into account the roughness of the wall by entering a tabular (theoretical) coefficient.
(6) Time-based pulse meter
This type of flowmeter is primarily intended for measurements in relatively clean flow, as the accuracy of their readings largely depends on the homogeneity of the medium. This type of device is often used to measure the flow of pure drinking water, or on water intakes. In the effluent part, they are commonly used on the sewers of industrial company cooling circuits, as well as for water treated in processing plant outlets. Their advantage is the ability to measure very wide channels – up to 100 meters or more. Pulse-time flow gauges are available with ladder or surface sensors for pressurized pipes, and for unsanthy pipes – in the form of wedge-shaped pipes or sensors, or hemispheres.
 |
 |
Installation of submersible sensors for wastewater meters (Open Channel Flow Meter)
If everything is clear enough with the installation of level meter proximity sensors and radar flow meters (ease of installation is their main advantage, thus reducing measurement accuracy), then the installation of immersion sensors often requires special technical solutions. In gravity pipes with a diameter of 200-800 mm, Doppler and cross correlation sensors are installed, in general, on the spacer mounting ring, which ensures a minimum installation time with reliable fixation.

In pipes with a diameter of more than 800 mm, plates with sensors are attached to the pipe wall. When installing in very dirty water, such as industrial waste or feces, you should carefully monitor the installation and installation of wires, especially at the bottom of the pipe. In addition to the fact that poorly attached wiring causes a buildup of hair, dirt and fabric on it (with the possibility of blockage or overall erosion of the structure by subsequent flow), the cable can dangle under the influence of flow and commotion during friction on the mounting structure. When attaching metal plates to large diameter pipe walls with screws, even the shape of the mounting screw head and many other technological details are essential.
A serious problem is the installation of immersion sensors in deep flow, especially at high flow rates and the inability to stop flow temporarily. For this, diving work or work with a minimum flow rate (at night, etc.) Can be used. However, there are specialized technical solutions that make it possible not only to lower the sensor into deep flow, but also to extract it from there without the help of divers for calibration and maintenance. The images below show the installation options for sensors on metal structures that can be lowered into the duct and removed from it.


In addition, the sensor can be mounted on an inverted float. This not only facilitates the installation of sensors in the inner channel, but also makes it possible to make accurate calculations for variable bottom sediments (in cases where the bottom sediment depends on the amount of rainfall, for example), because ultrasonic level gauges built into the sensor will measure the flow level from the surface. to the actual lower surface with sediment.

We can also mention the additional ability of cross-correlation flow meters to measure wide flow. This type of flow meter allows you to connect multiple speed sensors located at the bottom of the channel or at the bottom and on the wall of the channel to the computer and, therefore, get a speed diagram not only in the depth of the flow, but also in width. It provides high accuracy measurements in wide channels.

Possible problems when using a waste measuring device with a soak sensor
The most serious problems when using immersion sensors are the possible loss of efficiency due to pollution while working in dirty sewers, or destruction if there are rolling rocks and other heavy objects in the river. At the same time, Russian water companies are very serious about this problem, because they consider sewer pipes in our country to be the dirtiest. But that’s not the case. Diving sensors are used around the world, not only in well-maintained pipes in Germany and Switzerland, but also in India and other countries where sewage systems are no cleaner than domestic ones.
The ultrasonic sensors used are specifically designed for severe working conditions and do not lose work during siltation, because wet mud transmits ultrasound well.
When covering the sensor with a layer of cloth or opaque material to ultrasound, flowmeters from reputable manufacturers do not give incorrect readings, but signal errors and the need for cleaning. To reduce the chance of blockage, sensors are usually installed not at the bottom (not at 6 o’clock), but with some offsets (for example, at 4 or 5 o’clock).
 They also use installations at small heights (on special mounts) and a number of methods to minimize problems caused by dirt.
They also use installations at small heights (on special mounts) and a number of methods to minimize problems caused by dirt.

To protect against scroll stones and other solid objects that can damage the sensor house, special metal protectors are used.
Another problem is the measurement of currents that have low levels at some point in time. This leads to the fact that water does not cover the sensor and does not allow speed measurements. The possibility of transferring an unsanctated flow to a pressure flow through the use of a bent upward pipe has been described above. Small dams can also be used to raise levels. At the same time, the flow remained without pressure, but the level rose.
Open Channel Flow Meter Review of the most popular models and manufacturers.
Among the flow meters certified and used in Russia, the following manufacturers can be noted: Cross-correlation instruments are provided by Nivus GmbH.
Doppler flow gauges are supplied by several foreign companies and a number of domestic companies; Among the foreigners, Nivus (OCM-F), ISCO, ADS, Hydreka (Mainstream) can be noted; Domestic manufacturers “Up” and “Dnepr” themselves do not specifically recommend the purchase of their Doppler flow gauges, while to measure flow in open channels it is advisable to install level meters that are more familiar to their production.
Non-contact flow meters with functions measuring surface runoff velocity are offered by Nivus (OFR), FlowTronic (RavenEye), Hach (Flo-Dar). ISCO offers a non-contact laser flowmeter.
Devices for converting pressure-free flow to pressure flow are offered by Nivus (Profiler), Flow-Tronic (Sewer Mag) and domestic manufacturer Enrim (Stockmer).
Pulse flow meters for channels are offered by Nivus, Accusonic and Seba Hydrometrie.
Among the level meters with the function of measuring flow rate, the most popular manufacturers are Signur (Echo-R), Takeoff (RSL), Dnipro and many others. You can pay attention to the fully autonomous SonicSens level meter, operating on batteries from three to five years and transmitting information about levels and consumption via wireless GSM communication channels.
Open Channel Flow Meter Price for wastewater flow meter.
The current cross-correlation wastewater measurement device is the most accurate, reliable, and stable of all the flow meters available on the market. But the price is higher than the Doppler flow meter and, especially, the meter level. If you are dealing with small pipes, with small flows, and if the annual water cost for these meter units is much lower than the cost of a high-quality flowmeter, then it may be more profitable for you to use a cheaper (albeit less accurate) system – a level gauge or Doppler. At the same time, it is interesting that Nivus maintains Doppler flow meters of wastewater at a fairly low price than most foreign suppliers, due to the fact that Nivus focuses on the most reliable cross-correlation systems. As for channels with high consumption, for them the current method of cross-correlation is best.
Today there are many different wastewater meter options in price and quality. And if you are faced with the task of purchasing a meter for industrial, household or storm drains, or pipes and channels for intakes and spillways, then for each application you can choose your own version. At the same time, it is better to entrust the installation of waste measurement stations to specialists, because the accuracy of the readings and the length of their work depends greatly on the correct installation of the device.
Russian law on energy conservation requires companies and utilities to regulate wastewater calculations. Many are facing this question for the first time. First, you need to define the terms yourself and figure out how they were formed and the place where they went.
Wastewater is water contaminated by industrial waste and household waste, as well as water formed as a result of deposition in industrial facilities and settlements. Waste from the area is removed using a sewage system. It is a whole range of engineering equipment, facilities and sanitation measures that ensure the collection and disposal of waste, as well as its disinfection and treatment before it is discharged into a body of water or disposal.
There are two types of waste:
- internal;
- outside the room.
Internal systems are inside structures and buildings. It serves to collect and dispose of contaminated water into external sewer networks, where wastewater is transported outside the territory of industrial and residential facilities. Internal sewerage includes items such as bends, sanitary supplies, buildings and outlets from buildings.
Elements of external waste include pressure and gravity pipes, sewage treatment plants and sewage pumping stations, in other words, pumping stations.
Sewage systems imply the disposal of wastewater separately or together in the following categories: industrial, domestic and rainy. The sewage system itself can be separated and put together. In a separate system, clean production and rainwater are eliminated through one network, and domestic production and water – through another. Public systems for public networks of pipelines and pipelines dispose of all of the above categories of wastewater.
Accounting is done by state bodies. Installation, replacement, and inspection are also controlled by the state. Customers are required to provide representatives with access to plumbing and sewer devices. Vodokanal can’t do this for free. Therefore, water disposal services are paid in the same way as water services, that is, proportional to the volume of water discharged.
From the above it can be concluded that for all its cheapness (there is no cost to arrange accounting for contaminated water), it is estimated that wastewater is around. It cannot take into account consumer characteristics, which quite seriously affect the effluent/consumption ratio, both in one direction and the other. It should also be remembered that hot water consumed and consumed goes into the sewer. Such water suppliers are the most frequently different companies, while wastewater comes entirely from Vodokanal.
Imports, rainwater, which gets into the ground during a pipeline accident, is drained through the sewers and evaporated water is a “disturbing” factor. Because of them, the “consumption/waste” method works normally only for small consumers, for example, in the housing sector, who “traditionally” use water. In other cases, it is necessary to organize accounting using instruments.
Accounting for contaminated water will in some cases be beneficial to the party who disposed of it, and in some cases to the party involved in the disposal of the wastewater. Nevertheless, accounting will be “transparent” and objective in any case.
Method for drain head pressure accounting Open Channel Flow Meter
It has been mentioned that wastewater is transported through pressurized pipes and without pressure. The accounting systems of the two systems are slightly different. It is very easy to measure the volume of pressurized wastewater. The measurement of the volume of tap water (ordinary) from the wastewater measurement differs only in the second case, the flow rate is much lower, and the level of pollution is much greater.
As a rule, meter devices are installed in the outlet of the waste pumping station. Most often, their role is played by ultrasonic or electromagnetic flow meters. They are selected according to the range of costs measured. Ultrasonic devices can be used with surface sensors. To ensure stable operation (and reduce load on the pump), automatic air vents and check valves should be used.
Accounting for channels without pressure
A completely different and more difficult task is to calculate the drains without pressure. In this case, there are empty pipes or open channels where water flows at low speeds under the influence of gravity.
Specifically for this option, the variable rate method is created. In this case, the level meter is used as a flow meter. He recounted accounting information about the measurement section with “flow rate rate”. In this part role are trays parshal and venturi built into the channel. Bends with standard dimensions are also used. For them, the “level-flow” formula is obtained semi-empirically. This method works in U-shaped and unsanted pipes, and in this case bends and trays are not required. The methods described are governed by the State Standards document.
However, there are claims for this method. They arise due to the fact that the starting point in this method is the result of the characteristics of the previously calculated flow rate of the pipe, tray or shedding channel. The more accurate the initial calculation will be, the more accurate the device will work in the future. To determine the characteristics of a pressureless pipe or u-shaped channel, the flow rate of the fluid (provided that the level of filling is known) must be determined experimentally. Measurements are done “with the eyes”.
For example, you can use a piece that must be thrown into channels and watches. Such an attempted mistake is very bad. Therefore, there is another way – Shezy’s formula. Here, the coefficient of wall roughness and slope of pipe construction is considered. But these values can be called theoretical, because the real slope does not always correspond to that shown in the design documentation, and the roughness of the wall and its coefficients continue to change during the use of the pipe. Nonetheless, preliminary calculations are incorporated into the device. If errors are made in the source data, this can lead to inaccurate accounting. In many cases, these errors may go unnoticed. That’s why for the design and installation of measurement systems for channels without pressure, it is necessary to attract professionals.
Open Channel Flow Meter Domestic flow meter
Russian companies “Signur” and “Naik” produce devices that apply variable rate methods. These are ECHO-R-02 and Rise-RSL flowmeters. Levels are measured by non-contact methods thanks to ultrasonic sensors, which are located above pipes or channels.
Every device has its advantages and disadvantages. Benefit:
Deficiency:
- In the event of a flood, pipeline flood, or change in flow direction at the measurement site, the calculation becomes unreliable, since the flow level is the main measured parameter. If it remains unchanged, the device will show a flow rate corresponding to the “flow-level” chart point;
- 2 years is the period of inter-verification intervals;
- in sound guidance and AP, the formation of ice growth is possible;
- it takes a long straight.
The price of such a device is about 45,000 rubles.
The take-off-RSL flowmeter has the following advantages:
Despite all its advantages, “Takeoff-RSL”, like other flow meters, has disadvantages:
- Sensor radiation cones have differences. Therefore, reflection of various obstacles (stationary and non-stationary) can cause measurement errors;
- use of temperature correction. In an environment, the speed of ultrasound depends largely on temperature, composition, humidity and air pressure. It can also adjust the results.
The cost of such a flow meter is about 60,000 rubles.
Foreign devices
In addition to domestic manufacturers, flowmeters are produced by foreign companies. From foreign instruments to measuring costs in pressure-free pipes and open channels, there are instruments that apply the “area-speed” method. For example, Teledyne ISCO products. In such devices, the sensor is placed at the bottom of the channel and, using a pressure sensor, measures the water level above itself and the flow rate (using the Doppler method). Channel parameters must be entered into the device’s memory first. He compared this data with real-time information about the charging rate, after which the flow rate and flow volume were calculated. The main disadvantage of this method is its price, which is much higher than russian flowmeters.
It should be noted that for domestic and foreign devices, the main “enemies” are flooding and sediment formation in the measured location. In this case, the error increases. Therefore, the flowmeter, as well as its installation location, requires routine maintenance.
From the above, conclusions can be drawn. Until recently, wastewater accounting was a fairly urgent task. It can be solved by various methods. And if the pressure system is not problematic, then the system without pressure can be calculated in several ways. Consumers with small volumes of wastewater and a uniform ratio between consumed and polluted water can use the calculation method. The coefficient of ratio is determined empirically. But large consumers with changing or unclear “consumption/effluent” ratios should get instrumentation. Instruments that apply variable rate methods will be cheaper. But “area/speed” devices will be more expensive. In both cases, accounting nodes must be installed by professionals. They also need ongoing care.




