Insertion Flow Meter: Understanding, Functionality, and Application can provide a low-cost alternative to a full-flow drill device that can take up a lot of space, involves a lot of effort to install and presents special difficulties when it comes to service or calibration.
Definition of Insertion Flow Meter
The Insertion Flow Meter measures the speed of the liquid point in the pipe. Flow in very large pipes can be measured this way using relatively inexpensive gauges. There are two basic types of turbine insertion flow meters, axial (propeller type) and radial type (undershot water wheel). Overall accuracy is similar in both cases. In both types of turbines, the fluid velocity profile in the pipe must be “fully developed” because the arithmetic for the entire pipeline output is derived from this point flow measurement.
Upstream interference such as control valves, pipe bends, pumps and pressure regulators should be placed away from the flow meter insertion point, up to 100 pipe diameters in the worst case. Due to the relatively small interference that the measuring head causes to the pipe, the loss of pressure for this type of insertion flow gauge is so low that it saves energy by reducing pumping costs. Some types of self-powered insertion flow meter turbines allow their use in remote areas where power is an issue.
How An Insertion Flow Meter Works
Insertion Flow Meters are available in a choice of operating principles including Impeller, Turbine,Karman Vortex, Electromagnetic, Thermal Mass, and Pitot Tube. They all offer what is seen as the most important feature of the insertion flow gauge, which is that they can be incorporated into an existing pipe, with all the benefits that come with it (See Advantages below).
Basically a properly sized hole drilled into the pipe wall and a tool to secure the insertion meter is applied. This can be a saddle clamp, a welded threaded stubble or mating flange. The insertion meter is then inserted into the pipe to the depth suggested by the manufacturer, which can be adjusted to improve accuracy if calibration is in place permitting.
The meter, once secured will measure the speed only at this point and cannot calculate the volumetric flow until the diameter of the pipe and the nature of the medium are taken into account, usually in an electronic flow computer/display unit. The same can be said for mass flow models (multi-variables), as all variables need to be calculated using the corresponding gas or liquid equation, or enthalpy table in the case of steam.
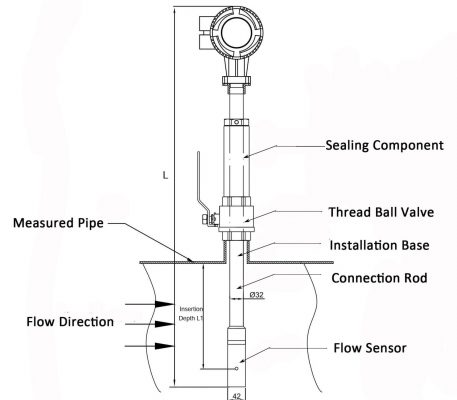
Example 1: Hot Tap Insertion flow gauge, combining ball valves in the assembly
Insertion Flow Meters serve a variety of markets including irrigation, HVAC, energy management, water treatment, firefighting equipment, and general industry. These gauges are often available in a choice of materials, styles and connection sizes with a wide variety of outputs and communication protocols.
Advantages of
Insertion Flow Meter
- Can be installed while the system is operating, without the distraction of “Hot-tap”
- Decreased Low Pressure
- Small physical size and weight
- Most styles don’t have moving parts.
- Quick and easy installation, compared to the installation of a full drill meter
- Suitable for very large pipes
- Easy to service and replace
- Lower cost than a full drill meter, especially at larger sizes
- Suitable for dangerous areas
- Battery Options Options
Disadvantages of
Insertion Flow Meter
- Lower Accuracy
- Affected by flow profile (required flow conditioning e.g., straight pipe length or diffuser)
- Measurement based on flow speed at inserted depth (Best average, depending on Reynolds number, media characteristic number, etc.)
- Remote viewing is often required due to the angle of insertion and accessibility.
Insertion Flow Meter application
- Boiler feed water
- Cold water
- Open and closed loop condenser water
- Irrigation system
- City water distribution
- Cooling process and flow
- Groundwater remediation
- Chemical processing
- Steam flow in the plant space
- Digester pump protection
- Bio-gas
- Mining wastewater
Coriolis Mass Flow Meter: Definitions, How It Works, and Benefits
Thus the article about insertion flow meter, hopefully can help and answer the questions of readers to related articles, hopefully useful.
