Turbine Flow Meter or Turbine Flow Meter (axial turbine) was invented by Reinhard Woltman and is an accurate and reliable flow meter for liquids and gases. This flow meter uses the mechanical energy of flowing fluid to rotate a “pinwheel” (rotor) translating the mechanical action of turbine rotation in the fluid flow around its axis into a readable flow rate (gpm, lpm, etc.) surroundings.
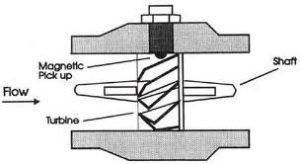
The blades on the rotor are tilted at a certain angle like a propeller, to convert the energy from the fluid flow into rotational energy. The rotor shaft rotates on a bushing/bearing where as the fluid moves faster, the rotor rotates proportionally faster.
This type of flow meter is widely used for the measurement of natural gas and liquid flow. Although measurements with turbine flow meters are less accurate than measurements with jets or displacements at low flow rates, the measuring elements do not occupy or disconnect from the entire flow path.
Turbine Flow Meter Characteristics
The shaft rotation of the Turbine Flow Meter can be sensed mechanically or by detecting blade motion. Blade motion is detected magnetically, with each blade or metal embedded piece generating a pulse.
When the liquid moves faster in the turbine flow meter, it will generate more pulses which will be proportional to the velocity of the fluid flow. Pick-up sensor on turbine flow meter will process pulse signal to determine fluid flow. Transmitters and motion systems are available to capture flow in both forward and reverse current directions.

The pick-up sensor generates pulses as fast as the impeller rotates, this provides a very fast reaction time which makes this type of flow meter very suitable for batching applications. The pulses generated by the pick-up sensor are pulses per unit volume, also referred to as the k-factor.
Turbine Flow Meter Function
Turbine Flow Meters can be used to measure the flow velocity of liquids, gases and vapors in pipelines, such as hydrocarbons, chemicals, water, cryogenic liquids, air, and industrial gases. It should be noted in determining the turbine flow meter should be careful on dirty liquids (containing garbage, sand and other solids).
Because the dirt that passes through it will be able to hamper accuracy and will even fail because the rotor can’t rotate due to getting stuck in dirt. Likewise for non-lubricating fluids, because the flowmeter may malfunction or its accuracy deviates too far because there are turbine flowmeters equipped with grease for use in fluids that do not have lubrication properties.
In addition, turbine flow meters designed for a specific purpose, eg for natural gas service, can often operate over a limited temperature range (eg up to 60 C) where operation at higher temperatures can damage the flowmeter.
This flow meter is better if applied to sanitary, relatively clean, and corrosive fluids in sizes up to about 24 inches. Small turbine flowmeters can be installed directly in the pipe, but the size and weight of larger turbine flowmeters may require the installation of a strong foundation.
Turbine Flow Meter Type
Turbine Flow Meters are generally available from 1.5 inches to 12 inches or larger pipe sizes. The turbine body is usually made of bronze or iron. The inside of the turbine can be non-corrosive plastic or metal, the turbine is accurate under normal working conditions.
In fire hydrants there is a special type of portable turbine flow meter that is placed on the hydrant to measure the water output of the hydrant. Usually made of lightweight aluminum with a capacity of 3 inches. Often used for the purposes of measuring water used in construction, filling swimming pools or where permanent measurements have not been installed.
At this time it has developed with various basic materials / materials from non-metal, carbon steel, brass, to stainless steel.
Turbine Flow Meter Applications
Turbine Flow meter applications are less accurate at low flow rates because they can slow down the rotation of the rotor. Meanwhile, for turbine flow meter installations there are inline using threaded flange connections and there are also those using the insert method, usually known as insertion turbine flow meters.

Likewise for fluid flow velocity that is too high on the Flow Meter Turbine can cause wear on the bushing or bearing or rotor shaft because it should operate flowmeters approximately 5 percent higher than the maximum flow speed as determined by the manufacturer.
In some applications, bearing replacements may need to be done regularly and result in high maintenance costs. Likewise, applications in dirty fluids should generally be avoided thereby reducing the possibility of flowmeter life time and bearing/shaft rotor damage, because turbine flowmeters have moving parts that wear out with time of use.
Meanwhile, in terms of materials for this type of turbine flow meter, there are quite a variety of materials ranging from carbon steel, stainless steel, both food grade and not, which are widely used for the food industry, even from non-metallic materials such as PVC, PP, Teflon and many others. used for chemical flow meters.
Important Factors In Turbine Flow Meter Operation
To obtain maximum output from the turbine flow meter, there are several important factors that need to be considered, for example a very low flow can affect the readings on the sensor because of the resistance in the rotor (less thrust). It is advisable not to operate the turbine meter at high speed as this may cause premature wear of the bearings, or may even cause damage.
It should also be noted that certain types of fluids can lubricate bearings, such as oil. However, if the fluid flowing does not support the occurrence of lubrication, then we should be aware of bearing wear, because bearing wear can reduce accuracy. In some applications, it is necessary to replace bearings regularly but of course it will also increase maintenance costs.
Applications for dirty liquids should be avoided, especially if the liquid is corrosive because it can damage the bearings. In short, turbine flow meters have moving parts that can degrade over time.
Selain itu, adanya transisi cairan dari cair ke gas secara mendadak harus dihindari karena secara mekanis dapat menekan flow meter, menurunkan akurasi, dan bahkan dapat merusak flow meter. Kondisi ini biasanya terjadi ketika mengisi pipa dan di bawah kondisi slug flow (aliran siput). Kondisi aliran dua fase juga perlu dihindari karena bisa menyebabkan turbine flow meter menghasilkan output yang tidak akurat.
In addition, sudden transitions of liquid from liquid to gas should be avoided because it can mechanically compress the flow meter, reduce accuracy, and even damage the flow meter. This condition usually occurs when filling the pipe and under slug flow conditions. Two-phase flow conditions also need to be avoided because they can cause the turbine flow meter to produce inaccurate outputs. The wheels of the Turbine Flow Meter are installed in the path of the flowing liquid and hit the turbine blades, exerting a force on the turbine blade surfaces and making the rotor move. When a constant constant rotational speed is achieved, the turbine speed is proportional to the fluid velocity.
The direction of flow is generally straight through the gauge, allowing for higher flow rates and less pressure loss than typical measurement types for commercial use, firefighting and as a master meter for water distribution systems.
Advantages of Turbine Flow Meter
Turbine flow meters have several advantages when compared to other types of flow meters. The advantages in question include:
- Has a turndown ratio of up to 35:1
- Wide flow rangeability, including for low flow rates
- Good level of accuracy
- Simple construction but good durability
- Ease of installation and maintenance
- Flexible connection to other flow instruments
- Can operate at various temperature and pressure conditions
- Low pressure drop across the turbine.
Disadvantages of Turbine Flow Meter
Apart from all the advantages of this flow meter as written above, this flow meter of course also has some drawbacks that can be taken into consideration. Some of these shortcomings include:
- Not suitable for handling highly corrosive liquids
- The presence of bubbles in the liquid can affect accuracy
- Requires constant back pressure to prevent cavitation (air bubbles)
- Sensitive to changes in fluid viscosity
- Requires a straight pipe network upstream and downstream of the turbine meter to dissipate the eddies in the liquid
- May not function properly in high viscosity fluids where the flow profile is layered
- Accuracy requires a turbulent flow profile where the fluid velocity is consistent across the entire pipe diameter
- Not suitable to be applied to liquids with solids in them (it is recommended to install a filter upstream before the liquid enters the flow meter).
