Introduction to electromagnetic flow meters.
Electromagnetic flow meter is a type of volumetric flowmeter. Electromagnetic flowmeters do not have any moving sensor components. Therefore, electromagnetic flow gauges are ideal for any dirty liquid that is conductive or water-based, such as: application of wastewater and sludge.
For those who care about changes in pressure, electromagnetic flow meters are ideal to use. Due to low pressure reduction and cheap maintenance or can be said to be free maintenance. Magnetic flowmeter type is also ideally applied
Electromagnetic flowmeters are often an option for certain applications. due to its construction properties that do not pose flow barriers and its low operating costs for aggressive chemical fluids and slurry. Electromagnetic flow meters provide highly accurate volumetric flow measurements. Accuracy over a wide flow range can be as good as ± 0.5% of the flowrate and can be better.
For the function and purpose of the electromagnetic flow meter installation has the following models:
Compact or Integral model where the displai or flow teransmitter or converter is fused with electromagnetic fow sensor and split or remote model where electromagnetic sensor is separated from the display. In terms of how the installation is also available the type of insertion flow meter where the way the flow sensor installation is enough to perforate the pipe and installed fittings to insert the sensor into the pipe.
Constructing electromagnetic flow meters can be custom by choosing the type of liner, electrode and body sensor material that is adjusted to the type of fluid and pipe used or field conditions.

How electromagnetic flow meters work
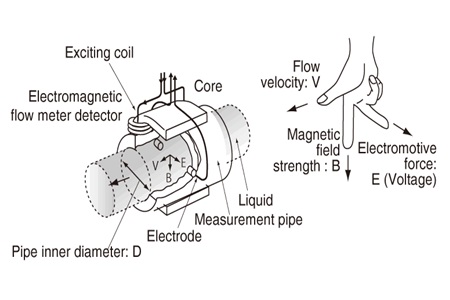
Electromagnetic flow meters use the principle of Faraday’s Law on Electromagnetic Induction to measure the rate of fluid flow in a pipe. In the magnetic flowmeter pipe, the magnetic field is generated, and channeled to the fluid flowing through the pipe. Faraday’s law states that the resulting voltage is proportional to the movement of a flowing liquid. A conductor moving through a magnetic field produces an electrical signal inside the conductor.
The signal generated is proportional to the speed at which water travels through the magnetic field. As the liquid flows through the magnetic field, the conductive particles in the liquid make changes. This variation is used to measure and calculate the speed of water flow through a sensor tube in the form of a pipe pipe. The resulting voltage will increase according to the increasing speed of movement of the liquid. The converter or electromagnetic flow transmitter will process the voltage signal to determine the flow of the liquid.
Faraday’s legal principles
Faraday
E’s formula is comparable to V x B x D where:
E = Voltage generated in
conductor V =
Conductor speed B = Strength of magnetic field D = Length of conductor
To apply the above principle to the flow measurement in electromagnetic flow meters, the first is to state that the liquid measured must be electrically conductive in order for the Faraday principle to be applied. As applied to the design of an ecmagnetic flowmeter, Faraday’s Law shows that: signal voltage (E) depends on V, B, D. where:
- V is the average speed of the liquid;
- B is the strength of the magnetic field;
- D is the length of the conductor (which in this case is the distance between the electrodes).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Advantages of using electromagnetic flowmeter
- Have high and stable precision or acurasi
- Can take two-way measurements
- Pressure drop is very small.
- No parts of the sensor component move or rotate.
- Can be used for sanitation, dirty water wastewater to sludge water
- It can be applied to beverage products, milk, sauce, soy sauce and other viscous ciaran that have adequate conductivity.
- Available from kicil size to DN2000
- Available power from AC, DC to battery
- Insertion flow meter is available
Disadvantages of using electromagnetic flowmeter
- Cannot be yellowed for liquids that do not sufficient conductivity
- Cannot be used in areas that have a high magnetic field
- Less precisely used in liquids that are very high in temperature
- Cannot measure pressure and temperature and needs to be installed its own sensors
How to Use electromagnetic Flow Meters
An electromagnetic flowmeter consists of two parts: electromagnetic flow sensor and electromagnetic flow transmitter or converter. Magnetic flow meters work Based on Faraday’s electromagnetic induction laws to measure the speed of conductive flows that produce volumetric flows from conductive fluids greater than 5μS/cm.
An electromagnetic flowmeter can also be used to measure the volumetric flow rate of a strong corrosive liquid. Such as strong acids and alkalis, and uniform liquid-solid two-phase suspension liquids such as sludge, pulp and pulp. It is widely used in liquids in pipes, such as water, acids, caustics, and porridge.
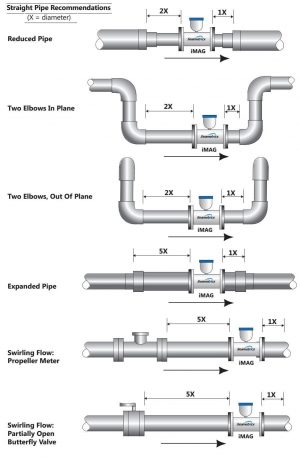
Electromagnetic flow meters do not require long upstream and downstream, so they can be installed on relatively short pipes by following the rules of manufacture. Usually inter-5 – 10 diameter upstream pipes and 2-5 Downstream pipe diameters
Magnetic Flow Meter Application
The construction of the magnetic flow meter that comes into contact with the fluid is the liner and electrode. Both of these parts can be made from materials that correspond to the type and characteristics of liquids that pass through electromagnetic flow sensors. The selection of this type of material from two parts must meet the properties of the liquid that is heat resistant, corrosive to abrasiv, so as not to contaminate the liquid that passes through the flow meter to maintain the quality of production.
Clean and Dirty Water
Electromagnetic flow meters can be used for PDAM water applications, river water, lake water, well water, wastewater, clean water in water treatment, pltu, to water for water in lake water or dams.
Chemical and corrosive Liquids
By paying attention to jneis electrode material and liner Flow meter electromagnetic can be used to measure the flow of highly corrosive liquids (such as acids and caustics) and abrasive pulp can be measured. Corrosive liquid applications are found in many industrial chemical processes, and in chemical liquid filling systems used in most industries.
Liquid Mud or porridge
Abrasive slurry applications are found in the mining, mineral treatment, and wastewater industries.
For abrasive and corrosive pulp media, such as in the kima process, it is necessary to pay attention to the selection of the type of material from the liner and electrode so that the flow meter is not quickly damaged.
Likewise, for the use of magnetic flow meters in thick liquids or porridge must be considered the speed of flow or flow velocity operates above 0.1 m / s. This is to avoid filling pipes with solids that can affect measurements and potentially stop the flow of mammoths.
The use of electromagnetic flow meters in streams without pumps or gravity flow that needs to be considered be sure the orientation of the flowmeter is such that the flowmeter is filled with fluid. Failure to ensure the flowmeter is filled with fluid can affect flow measurement.
Types of Industries that use electromagnetic flow meters
- Pulp and paper industry;
- Metal and mining industries;
- Water Treatment and Wastewater Treatment;
- Food and beverage processing industry;
- Chemicals industry;
- Petrochemicals;
- Oil and gas.
- Hospitality dna Hospital
- PLTU
- Palm Oil Industry
- Dll
